In the Ganzhou Basin of Ganzhou city, located in China’s Jiangxi Province, researchers have uncovered two fossils that contain the most comprehensive duck-billed dinosaur embryo ever documented scientifically. These remarkable embryo specimens are currently housed in a section of the Fujian Science and Technology Museum.
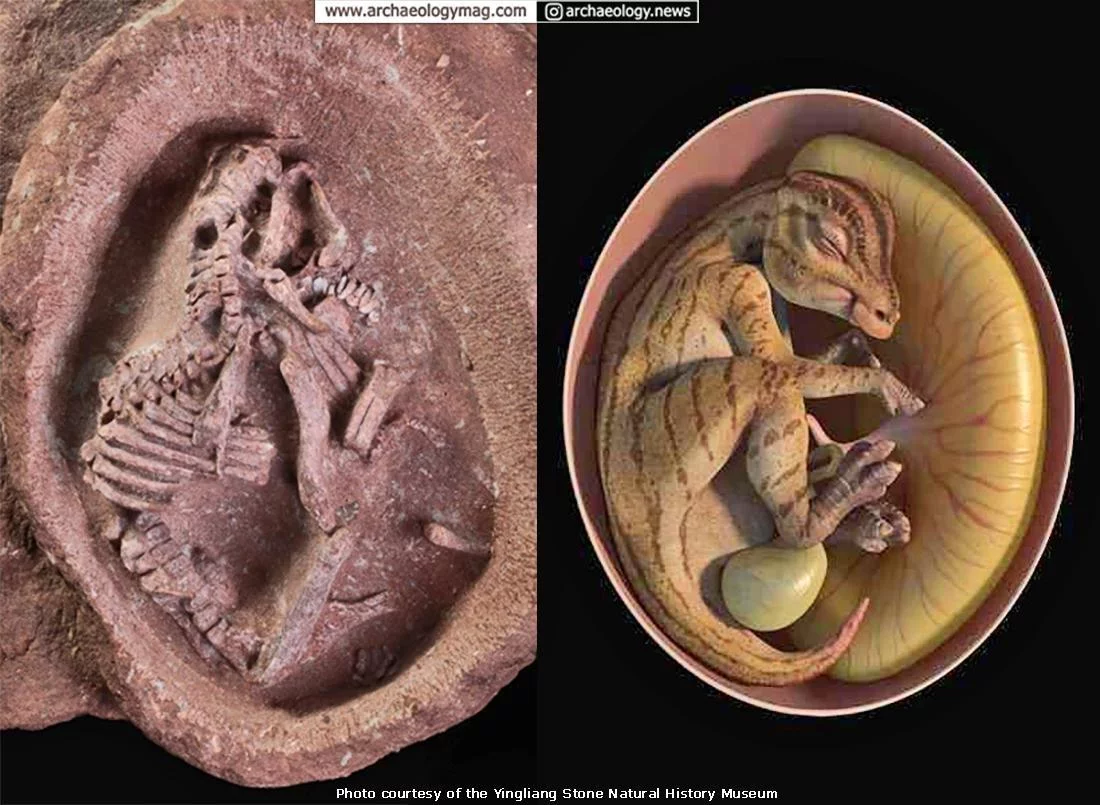
The dinosaur in question belongs to the category of giant herbivores that thrived toward the conclusion of the dinosaur era. While prior discoveries have yielded similar embryos, the Ying Baby, as it has been named, stands out as the best-preserved example to date.
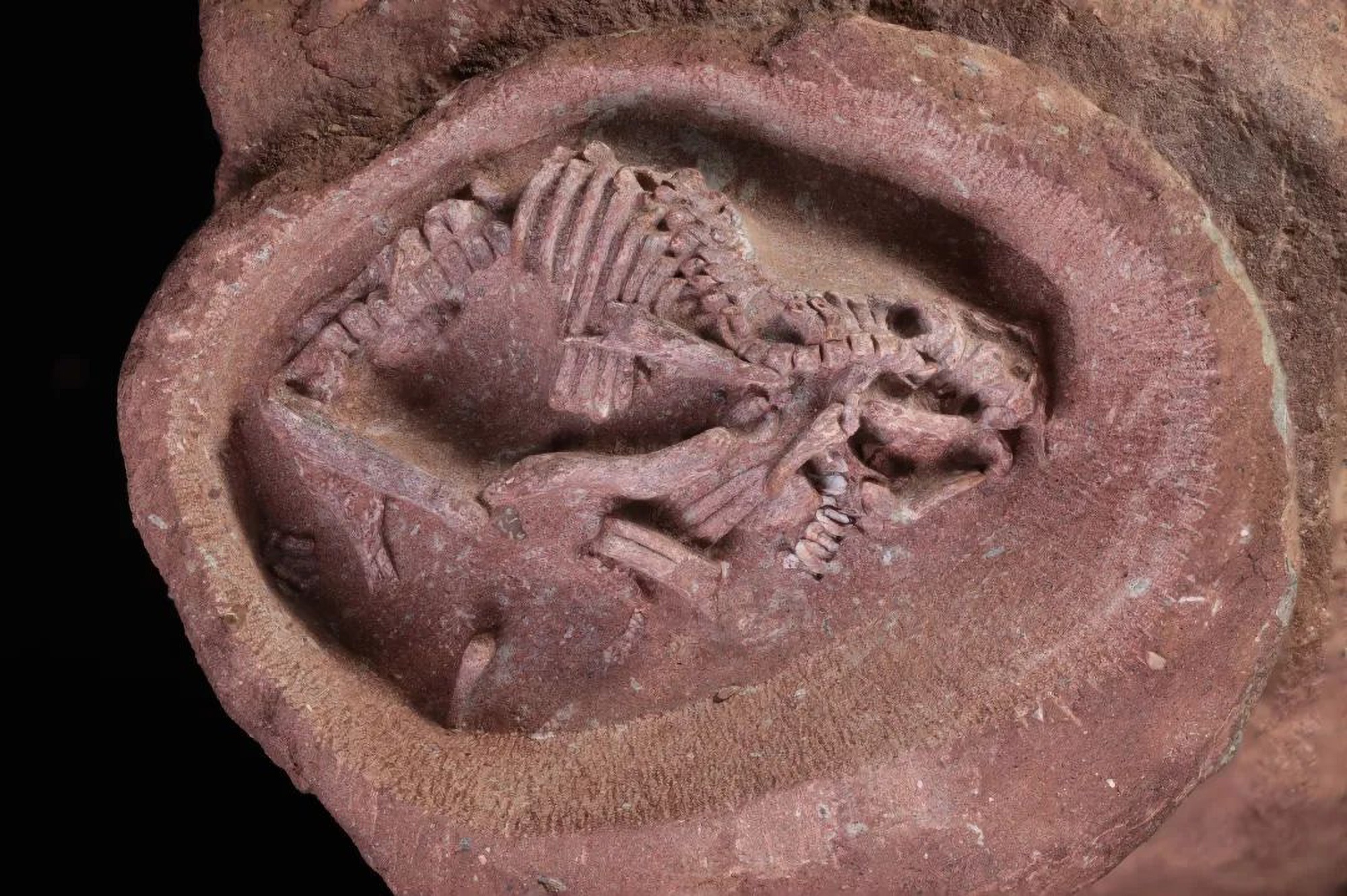
The dinosaur egg enveloping the embryo takes on the shape of an ellipsoid and measures approximately 9 centimeters in length. This egg was unearthed from the Late Cretaceous strata in the southern reaches of Jiangxi Province, boasting an age that dates back 66 million to 72 million years.

At present, the Ying Baby is held at the Yingliang Stone Natural History Museum in Fujian Province, East China. This discovery significantly contributes to our understanding of dinosaur reproductive development, behavior, evolution, and paleoecology, offering valuable insights into these creatures that inhabited the planet during the final stages of the dinosaur era.
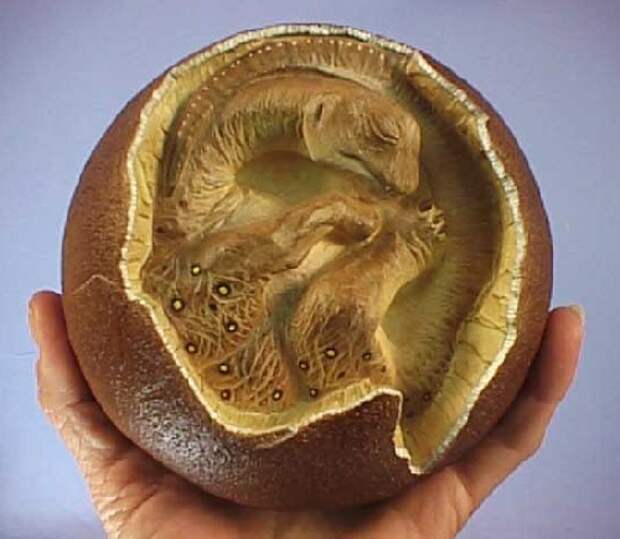

A particularly noteworthy revelation from this discovery is the small size of both the egg and the embryo, suggesting that duck-billed dinosaurs inherently possessed diminutive eggs and underwent late-stage body development as a fundamental characteristic of their species.




